Cardiovascular system Atherosclerosis
The atherosclerosis is a process of artery aging. Atheroma (fat) plaques are forming inside the arteries as the time passes. With such plaques, the vessel reduces its internal diameter, causing difficulty for the blood passage.
The atherosclerosis may occur in several territories in the body, such as heart, brain, kidneys, intestine, legs, etc, compromising the circulation in the affected organ.
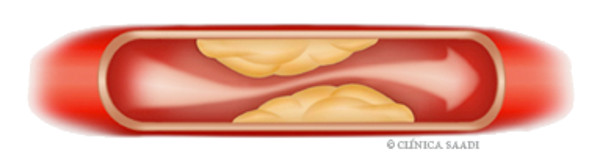
The cause of the atherosclerosis may be hereditary or be associated to the so-called risk factors, such as smoking, high pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle. There are also inflammatory processes in such atheroma plaques that can cause their destabilization, with a rapid increase in the narrowing or thrombosis degree (clot), causing symptoms such as, for example: ischemic cardiopathy, stroke, ischemia (reduction in blood flow) in the legs, among others.
Treatments
As the atherosclerosis is a generalized process that can affect several organs and systems, it must be treated in all patients with disease diagnoses. Diet low in animal fat, medicines such as antiplatelet-aggregation drugs to thin the blood and prevent thrombosis, and strict cholesterol control (by diet, exercise, and medication – stannines – if necessary) are measures that must be strictly considered in all patients with disease signs. First of all, the atherosclerosis must be prevented or delayed by controlling the risk factors.
Support notes
Risk factors: There are numberless scientific studies that identify several factors that increase the atherosclerosis risk. Click here to go to the page of Care and Prevention and to know more about this subject.
Ischemic cardiopathy: Also called coronary arterial disease, is the term used to define the narrowing of the coronary arteries caused by an atherosclerosis. Click here to go to the page of Ischemic cardiopathy and to know more about this subject.
Stroke: Disease caused by an impairment in the brain circulation, a consequence of the formation of fat plaques inside the carotid arteries.

